4751. Diagonals
In the n × n square table, find the sum of the numbers located on the main and
secondary diagonals.
Input. The first line
contains an integer n (1 ≤ n
≤ 500). The following n × n matrix consists of integers, each with
an absolute value not exceeding 105.
Output. Print the sum of
the numbers on the main and secondary diagonals of the matrix.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 3 2 5 4 8 7 9 3 |
15 21 |
SOLUTION
2-dim array
Algorithm analysis
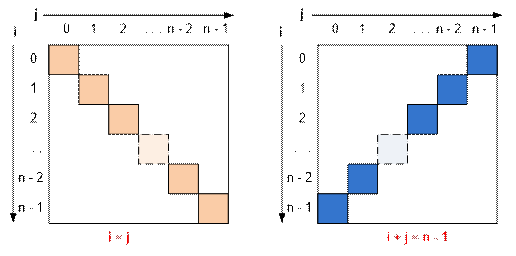
Let m be a given
two-dimensional array with zero-based indexing. The element m[i][j] belongs to:
·
the main diagonal if i = j;
·
the secondary diagonal if i + j = n – 1;
Example
Let’s consider the given example.
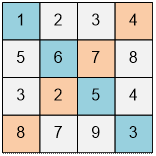
The sum of the integers on the main
diagonal is 1 + 6 + 5 + 3 = 15.
The sum of the integers on the secondary diagonal is 8 + 2 + 7 + 4 = 21.
Algorithm implementation
Read the input data. The matrix elements are processed on the fly, without
creating a two-dimensional array beforehand.
scanf("%d",&n);
a = b = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&val);
In the variable a, compute the sum of the elements on the main
diagonal.
In the variable b, compute the sum of the elements on the secondary
diagonal.
if (i == j) a
+= val;
if (i + j ==
n - 1) b += val;
}
Print the answer.
printf("%d %d\n",a,b);
Algorithm implementation – two-dimensional
array
Declare a
two-dimensional array.
int m[510][510];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
scanf("%d",
&m[i][j]);
In the variable a, compute the sum of the elements on the main
diagonal.
In the variable b, compute the sum of the elements on the secondary
diagonal.
a = b = 0;
Iterate through all the elements of the two-dimensional array.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
The element m[i][j]
is on the
main diagonal if i = j;
if (i == j) a += m[i][j];
The element m[i][j]
is on the
secondary diagonal if i + j = n
– 1;
if (i + j == n - 1) b += m[i][j];
}
Print the answer.
printf("%d %d\n", a, b);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[][]
= new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0;
j < n; j++)
m[i][j] = con.nextInt();
int a = 0,
b = 0;
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0;
j < n; j++)
{
if (i == j) a += m[i][j];
if (i + j == n - 1)
b += m[i][j];
}
System.out.println(a + "
" + b);
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – on the fly
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int a = 0,
b = 0;
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0;
j < n; j++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
if (i == j) a += val;
if (i + j == n - 1)
b += val;
}
System.out.println(a + "
" + b);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
m = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in
range(n)]
In the variable a, compute the sum of the elements on the main
diagonal.
In the variable b, compute the sum of the elements on the secondary
diagonal.
a = b = 0
Iterate through all the elements of the two-dimensional array.
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
The element m[i][j]
is on the
main diagonal if i = j;
if i == j: a += m[i][j]
The element m[i][j]
is on the
secondary diagonal if i + j = n
– 1;
if i + j == n - 1: b +=
m[i][j]
Print the answer.
print(a, b)
Python implementation – list comprehension
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
m = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in
range(n)]
In the variable a, compute the sum of the elements on the main
diagonal.
In the variable b, compute the sum of the elements on the secondary
diagonal.
a = sum(m[i][i] for
i in range(n))
b = sum(m[i][n - 1
- i] for i in
range(n))
Print the answer.
print(a, b)